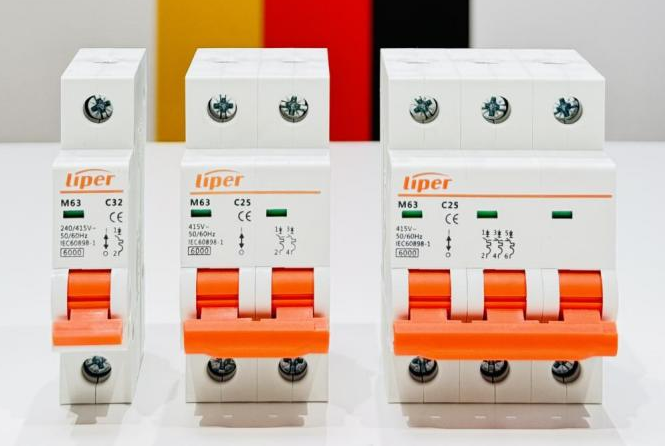
Circuit breakers are made in varying current ratings, from devices that protect low-current circuits or individual household appliances, to switchgear designed to protect high-voltage circuits feeding an entire city.
Liper makes Miniature circuit breaker (MCB) - rated current up to 63 A, which is often used in residential, commercial, industrial lighting.
MCBs are usually not destroyed during over-current so they are reusable. They are also much easier to use, offering the convenience of 'on/off switching' for circuit isolation and since the conductor is housed within a plastic casing, they are much safer to use and operate.
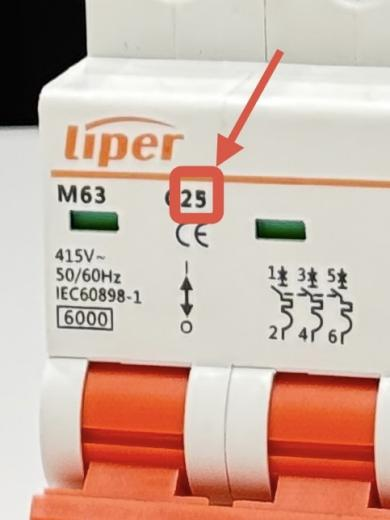
An MCB has three principle characteristics, Amperes, Kilo Amperes and Tripping Curve

Overload Current Rating - Amperes (A)
Overload occurs when too many appliances are put on one circuit and draw more electrical current than that circuit and cable are designed to take. This could occur in the kitchen, for example when the kettle, dishwasher, electric hob, microwave and blender are all in use simultaneously. The MCB on this circuit cuts power thus preventing overheating and fire in the cable and terminals.
Some standards:
6 Amp - standard lighting circuits
10 Amp - large lighting circuits
16 Amp and 20 Amp - Immersion heaters and boilers
32 Amp - Ring Final. The technical term for your power circuit or sockets. A two bedroom house for example may have 2 x 32A power circuits to separate upstairs and downstairs sockets. Larger dwellings can have any number of 32 A circuits.
40 Amp - Cookers / electric hobs / small showers
50 Amp - 10kw Electric showers / Hot tubs.
63 Amp - the whole house
Liper Breakers cover the range from 1A to 63A

Short Circuit Rating - Kilo Amperes (kA)
Short Circuit is the result of a fault somewhere in the electrical circuit or appliance and is potentially much more dangerous than overload.
MCBs used in domestic installations are typically rated at 6kA or 6000 amps. The relationship between normal voltage (240V) and typical domestic appliance power ratings mean that the over-current caused by short circuit should not exceed 6000 amps. However, in commercial and industrial situations, when using 415V and large machinery, it is necessary to use 10kA rated MCBs.
Tripping Curve
The 'Tripping Curve' of an MCB allows for real world and sometimes entirely necessary, surges in power. For instance, inn commercial environments, large machines usually require an initial surge of power in excess of their normal running current to overcome the inertia of large motors. This brief surge lasting just seconds, is allowed by the MCB as it is safe in a very short time.
There are three principle Curve Types which allow for the surges in different electrical environments:
Type B MCBs are used in domestic circuit protection where there is little need for surge permission. Any large surge in a domestic environment is likely to be the result of a fault, so the amount of over current allowed is relatively small.

Type C MCBs trips between 5 and 10 times full load current and are used in commercial and light industrial environments which may feature large fluorescent lighting circuits, transformers and IT equipment such as servers, PCs and printers.
Type D MCBs are used in heavy industrial facilities such as factories using large winding motors, X-ray machines or compressors.
All three types of MCBs provide tripping protection within one tenth of a second. That is to say, once the overload and period have been exceeded, the MCB trips within 0.1 seconds.
Therefore, Liper always meet all your needs.
Post time: Dec-04-2024